
Introduction
A website is a busy runway for all the traffic from different social media and advertising platforms. Businesses use websites for various services and products. As the digital realm is expanding with increasing users and social media platforms, it is imperative for a business to monitor and segment its ongoing user traffic and data generated. Digital Marketers specialized in analysis and marketing understand this very well and do extensive work to maintain and manage this data. To segment traffic from socials like Facebook or LinkedIn a website developer uses snippets of codes or marketing tags modifying website codes.This requires a good knowledge of coding and with every modification you risk losing website elements. To counter this issue a free product from Google called Google Tag Manager is used.
With this blog we aim to give you a clear view of Google Tag Manager features, benefits and ways to install it. As some of you might have heard about the newest analytics tool from Google- Google Analytics 4; we will talk in length about GA4 installation with Google Tag Manager and its remarkable benefits.
But wait, are you aware of Google Tag Manager? If not why not lets begin with the basics
What is Google Tag Manager?
Google Tag Manager is a free Google product which behaves as a central tag management system which has a highly attractive and interactive dashboard. It is a boon for non coders as well as Digital Marketers as the software injects tags automatically wherever and whenever necessary. So it definitely solves losing or breaking elements within website code while testing.
How does one install such a useful system?
- To set up,log in to your Google Account –> Tag Manage
- – Click “Create Account”
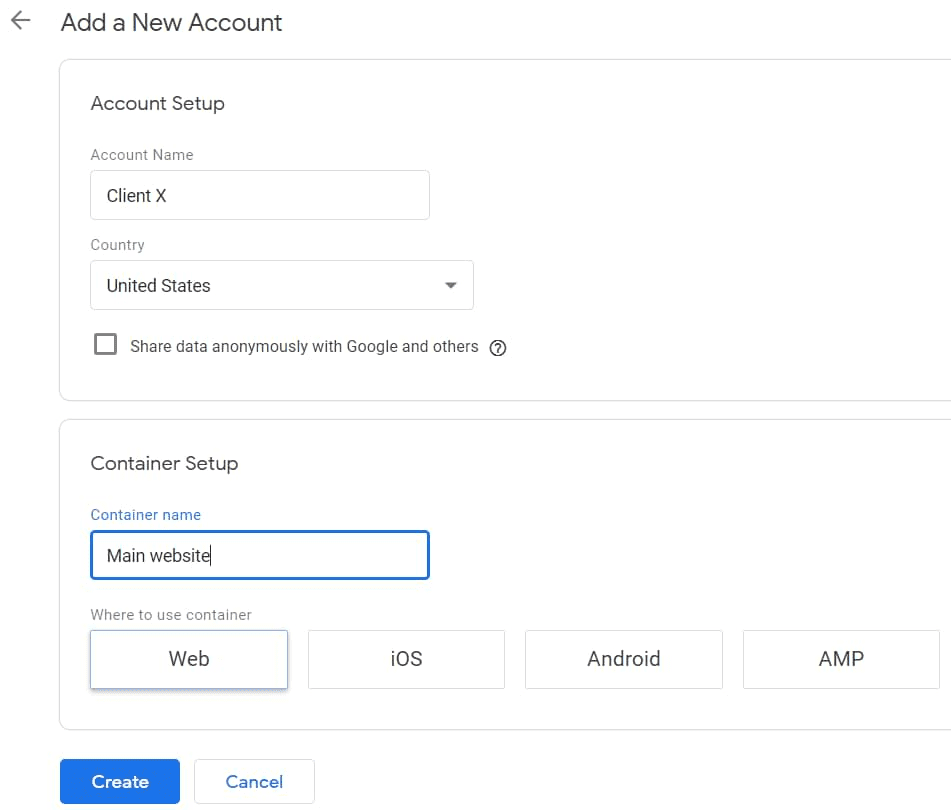
– Enter details required
Tip-Use your business name as your account name
-Create one account for one or multiple websites.
-Next, Enter a “Container name”
Hint- Container will be your website name, as it is the piece of code used you add for Google Tag Manager to work.
– Now, select “Target platform”

Tip- Your target platform will vary for web/mobile devices. So, use the web for websites, ios or Android for mobile devices.
– Click “Create” and your account is ready.
– Now, Modify website code yourself or with assistance and start using Google Tag Manager.
Tip– Place first code snippet in the <head> section as it uses JavaScript for extracting information.
– Place the HTML iframe code snippet in the <body> tag on the webpage.
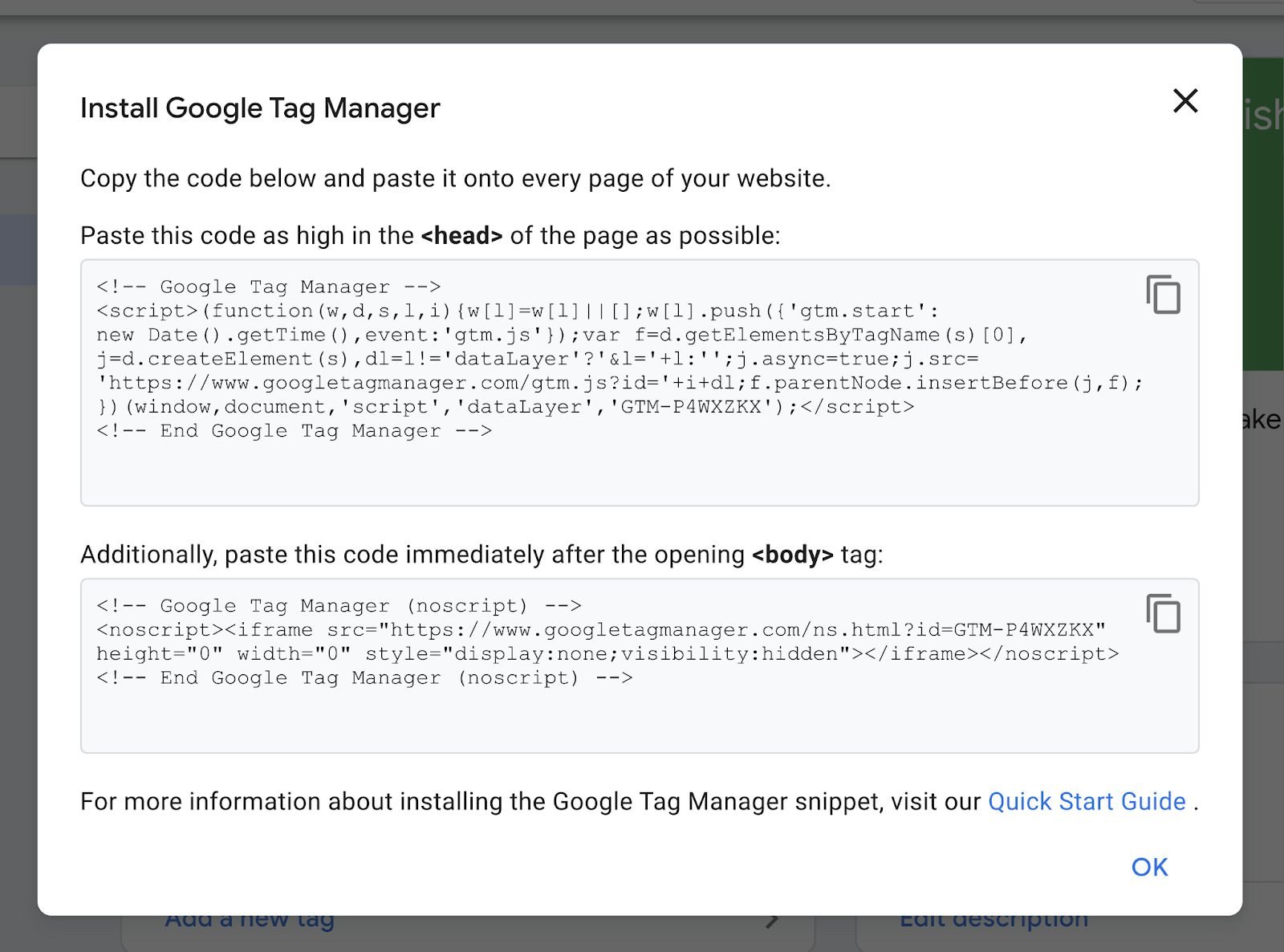
Your Google Tag Manager is all set for use. And the dashboard will look something like the image below.

Now, allow us to shed some light on the features of this Dashboard
Features of Google Tag Manager
Tags
Snippets of codes from analytics, marketing and other platforms are known as Tags. These Tags are primarily used to integrate with various sites and applications.
It will be easy to understand with an example
Google Tags are used by Google Analytics, it sends data from your website to a linked Google Analytics property.
The best part of Google Tag Manager is that you can create,manage and publish tags without writing a code! Woohoo for the non-coders!
Few commonly used Tags are:
Google Analytics
Google Ads Conversion Tracking
Pinterest Tags
LinkedIn Insight
Facebook/Meta Pixel
Triggers
As you already know Tags automatically fire when necessary, some trigger is needed to inject these Tags.
So, Triggers are the instructions for Tags to fire.
By definition Triggers are instructions so they are set for some actions taken on the website.So, you have to assign Triggers to each Tag to fire it up.
Few commonly used Triggers are
Page Views
Submission CTAs
Link Clicks
Time Spent on page
Variables
Additional pieces of particulars that Google Tag Manager might need to fire a Tag or Trigger.
They provide precision to Triggers/Tags.
An example will help you to understand it better.
“Google Analytics Settings” and “Constant” are commonly used variables. They define account IDs of Google Analytics(It is called “Measurement ID in GA4)
By creating a Variable that remembers your Measurement ID will allow you to simply click and attach it to new Tags that you create. This saves a tonne of time and reduces errors on your part.
Google Tag Manager comes with Pre-made Variables for your convenience. Plus, you can define variables as required.
Few Commonly Used Variables are:
-Google Analytics Settings
-Constant
-Page URL
-Form ID
These particulars will help you navigate the GTM Dashboard effectively and error free.
Benefits of Using Google Tag Manager
With such useful features at hand you must be curious about the benefits Google Tag Manager has to offer. Here they are:
- Free
Google Tag Manager is a FREE tool that means you don’t have to spend more to use its features.
- Easy Integration-
GTM integrates easily, saving time on management. You simply drag and drop for implementation.
- Saves Time-
You don’t have to write codes so it saves time and dependency on website developers; you can do it all by yourself.
4.Full Control-
You have full control over it; no one can make changes without your approval.
5.Testing of Tags-
You get to test, preview and debug Tags before deploying them.
6.Team Accessibility-
You can share accessibility with your team members, saving further time by assigning tasks.
7.Version Log-
GTM creates and logs versions of codes whenever you make changes. This gives you a full view of past and current versions easily.
Now don’t confuse Google Tag Manager with Google Analytics. But if you are already confused, read the difference between the two.
Read About Differences Between Google Tag Manager and Google Analytics
Look at the table below
| GOOGLE TAG MANAGER | GOOGLE ANALYTICS |
| It is a management system | It is a tool |
| No reporting feature to analyze data | All reporting features to analyze data |
| Used to manage which Tags will fire and when will fire using Triggers | Used to track interaction of user with a website |
Now that you know the difference it is important to know that Google Analytics has a new version called Google Analytics 4 or GA4.
Previous version known as Universal Analytics has a bit different setting GTM but with GA4 it is quite easy.
GA4 Setup with GTM

It is very easy to set up Google Analytics 4 with Google Tag Manager.
Simply follow four steps of create Trigger, create Tag, Publish and Test
Let’s go through each step
-
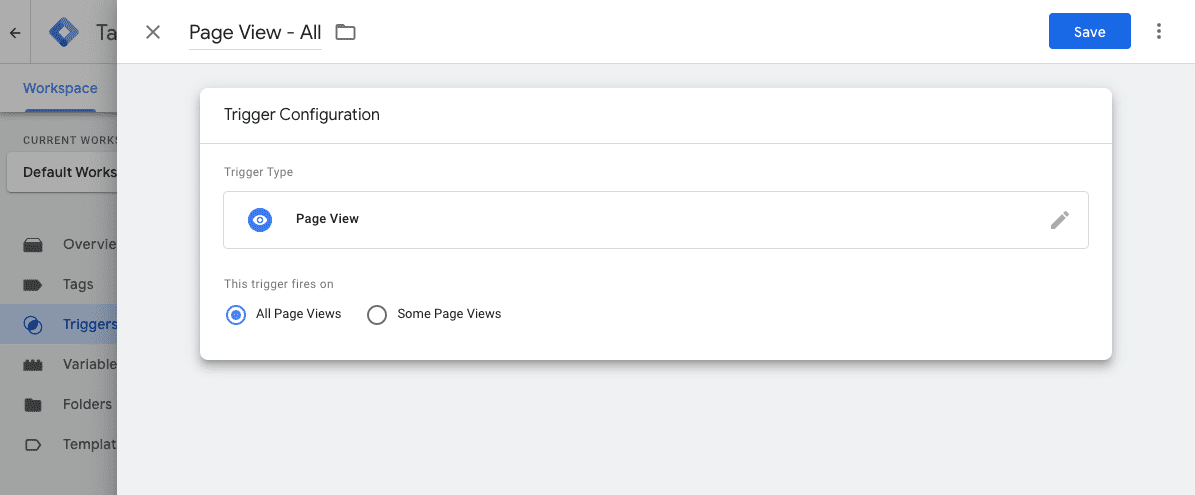
Create Trigger for GA4 in GTM
Open Google Tag Manager- Click”Triggers” (left-hand navigation bar) – Click “New”
Name the Trigger
Within the Trigger Configuration box select whichever type you wish to see and Save.
With this you have instructed Google Tag Manager to run tags associated with the Trigger you just created.
Below you will find an image showing an example trigger called” Page View”
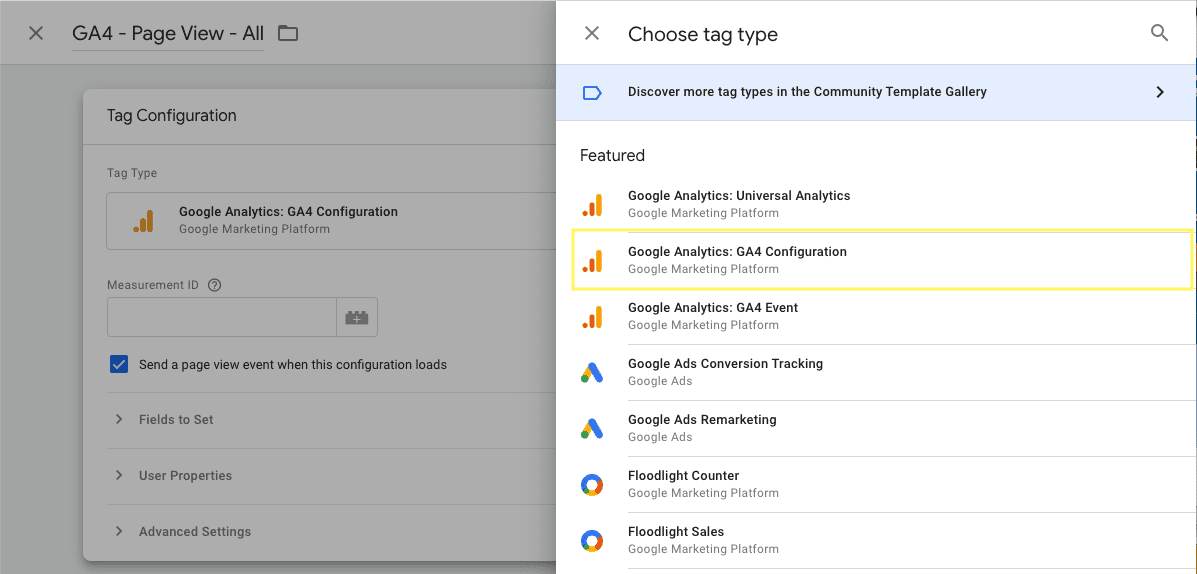
2. Create Tag for GA4 in GTM
For Trigger to deploy you need a Tag.
Open Tags(again left-hand navigation bar)- Click “New”
Name the Tag
Within the Tag Configuration box select from featured tags type you wish to fire and Save.
Enter your GA4 Measurement ID.
Now, select the Trigger you just made in step 1.
Your GA4 configuration Tag is ready to use.
Below you will find an image showing an example tag called”GA4 Config.”
But wait, are you sure you know where to find a Measurement ID?
No…?
It is available on GA4 Property- In the Admin section- Under “Data Streams” you will find your Measurement ID- Copy it.

3.Publish GTM Container
Now Publish the GTM Container with added Tag and Trigger to make it live.
Click”Submit”(Top right Corner of GTM Workspace)

4. Test GA4 Configuration
Actual data may take up to 24 hours or more to start reflecting but you can always test the setup.
Go to Tag Manager-Click”Preview”

Double check everything and you have configured GA4 to your website.
As many of you might still be using Universal Analytics it is advisable to go through the benefits of GA4 over UA. Read them now.
Read About Benefits of Google Analytics 4 over Universal Analytics

- Architecture
GA4 has an improved design. GA4 is built around events contrary to Universal Analytics that was based on sessions, which are like a series of page views. Events can vary from pageviews to clicks, form submissions or even custom events which you can define yourself. This augmentation allows GA$ to collect more data and provide insights into user actions other than pageviews.
- Cross-Platform Tracking
Users interact with a brand or business across various platforms like websites or mobile apps. Businesses need the data to understand user behavior. GA4 is great at tracking users across different devices and platforms. Businesses can create ‘data streams’ to see the traffic flow from web, app or specific locations. It makes data handling and tracking much easier and faster than Universal Analytics.
- Analytics and Reporting
GA4 can give you a thorough analysis of your data based on specific pages or events. It has been possible with its newest feature of reporting sections along with advanced analysis tools. And if a business wants to deep dive even more, it can export data to BigQuery, which is a powerful data warehouse service by Google.
- BigQuery Integration
Big Query is not your average run of the mill analyzer. It is capable of running complex queries using SQL or machine learning to find hidden insights in the data. It comes with virtually unlimited storage. BigQuery is like a turbocharged analytics engine at your disposal.
- Machine Learning
Insights are crucial for data analytics. GA4 can use machine learning to deliver smarter insights. It uses technique probabilistic matching to combine data from various resources. What this means is you can now combine data from different ad campaigns like Google Ads and Facebook Ads, GA4 can match the data from both sources and give you a single view of the performance.
- Improved Data Model
GA4 has a better and improved data collection model. A business can track actual searches on their website, regardless of the page the user is on. Another feature is tracking of offline conversions or in-app purchases. This upgrade gives GA4 an upper hand in accuracy and flexibility.
- Purchase Probability and Churn Prediction
Machine learning algorithms analyze individual user behavior and based on that GA4 can predict user purchase probability. Whether a user will likely make a purchase or churn (stopping using services/product).
Closing Thoughts
Guide to GA4 Migration and Setup with Google Tag Manager is your manual+brochure in a way that helps you learn Google Tag Manager and GA4 setup with GTM. We hope it benefits you and keeps you ahead in your analysis and marketing tasks. If you need more resources on the subject we have a pool of them to share with you. Find them here.
Check our latest Blog on What Makes INP Different from FID in Core Web Vitals, and Why Should SEO Experts Care?



